From Olive To Coconut: Discover The Best Cooking Oils For Every Dish
In the dynamic world of culinary arts the choice of cooking oil can make a significant difference in the flavor nutrition and overall quality of your dishes. As we enter 2024 the array of available oils has expanded offering a plethora of choices for home cooks and professional chefs alike. From the rich nutty flavors of sesame oil ideal for Asian cuisine to the robustness of extra virgin olive oil perfect for Mediterranean dishes each oil brings its unique character to the table. However with so many options it can be challenging to determine which oil is best suited for a particular cooking method or recipe. Whether you're deep frying sautéing baking or dressing salads understanding the properties of different oils – such as smoke point flavor profile and health benefits – is essential. This guide delves into the best cooking oils for various culinary applications helping you to elevate your cooking game by matching the right oil to every dish.
Types Of Cooking Oil You Can Consider For Best Cooking Result
Choosing the right cooking oil can feel like deciphering a cryptic code at the grocery store. With aisles lined with bottles boasting diverse claims it's easy to get overwhelmed. But fear not for beneath the glossy labels lies a fascinating world of fats flavors and potential health benefits! Let's dive into some of the most popular cooking oils explore their composition and understand how they can fuel your body and your culinary creations.
1. Olive Oil:
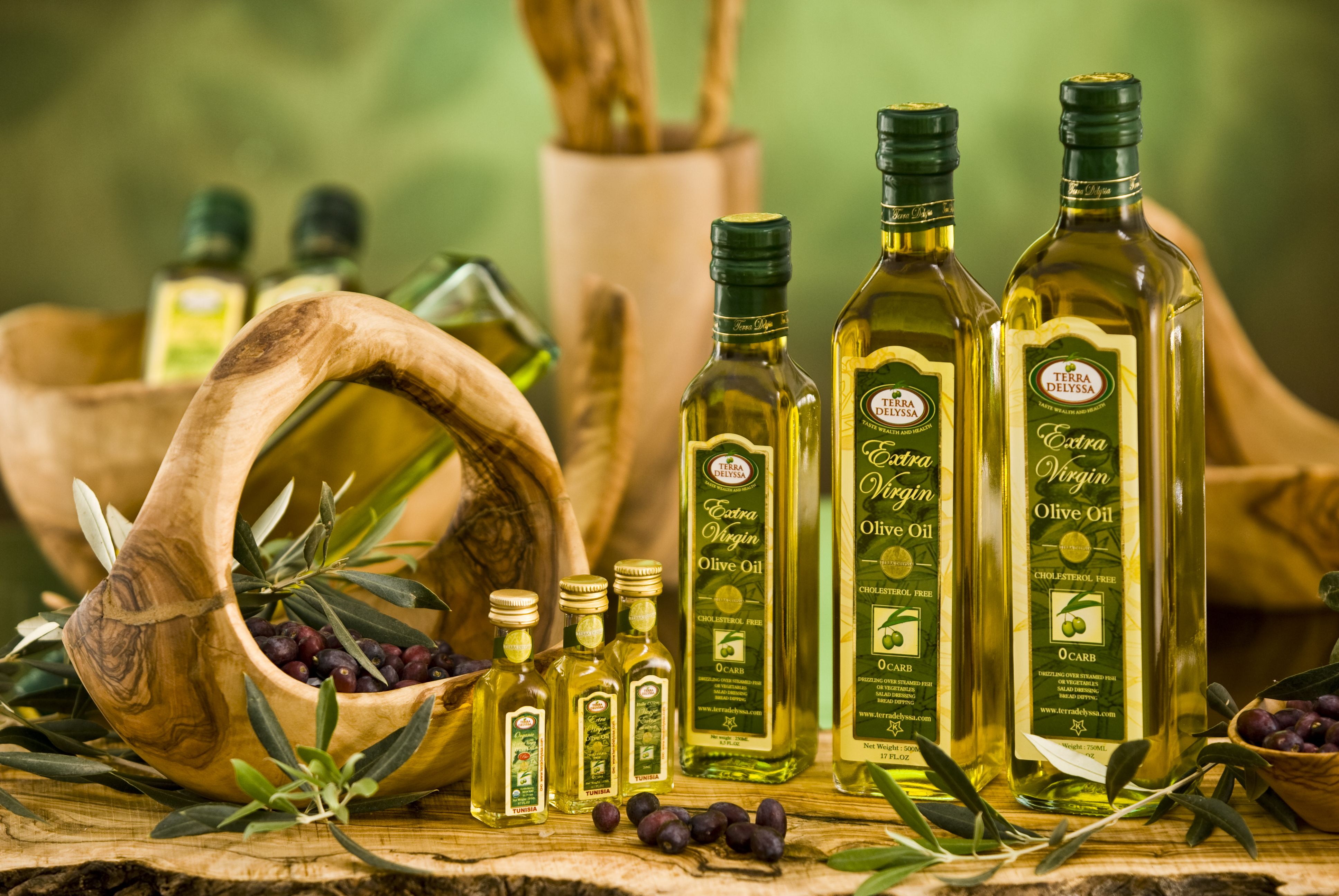

The crown jewel of the Mediterranean diet olive oil reigns supreme for its heart-healthy monounsaturated fats particularly oleic acid. This superstar fat lowers bad cholesterol (LDL) while raising good cholesterol (HDL) reducing inflammation and potentially protecting against Alzheimer's and certain cancers. Extra virgin olive oil minimally processed and pressed from fresh olives is the king of flavor perfect for drizzling dipping and low-heat cooking.
2. Avocado Oil:
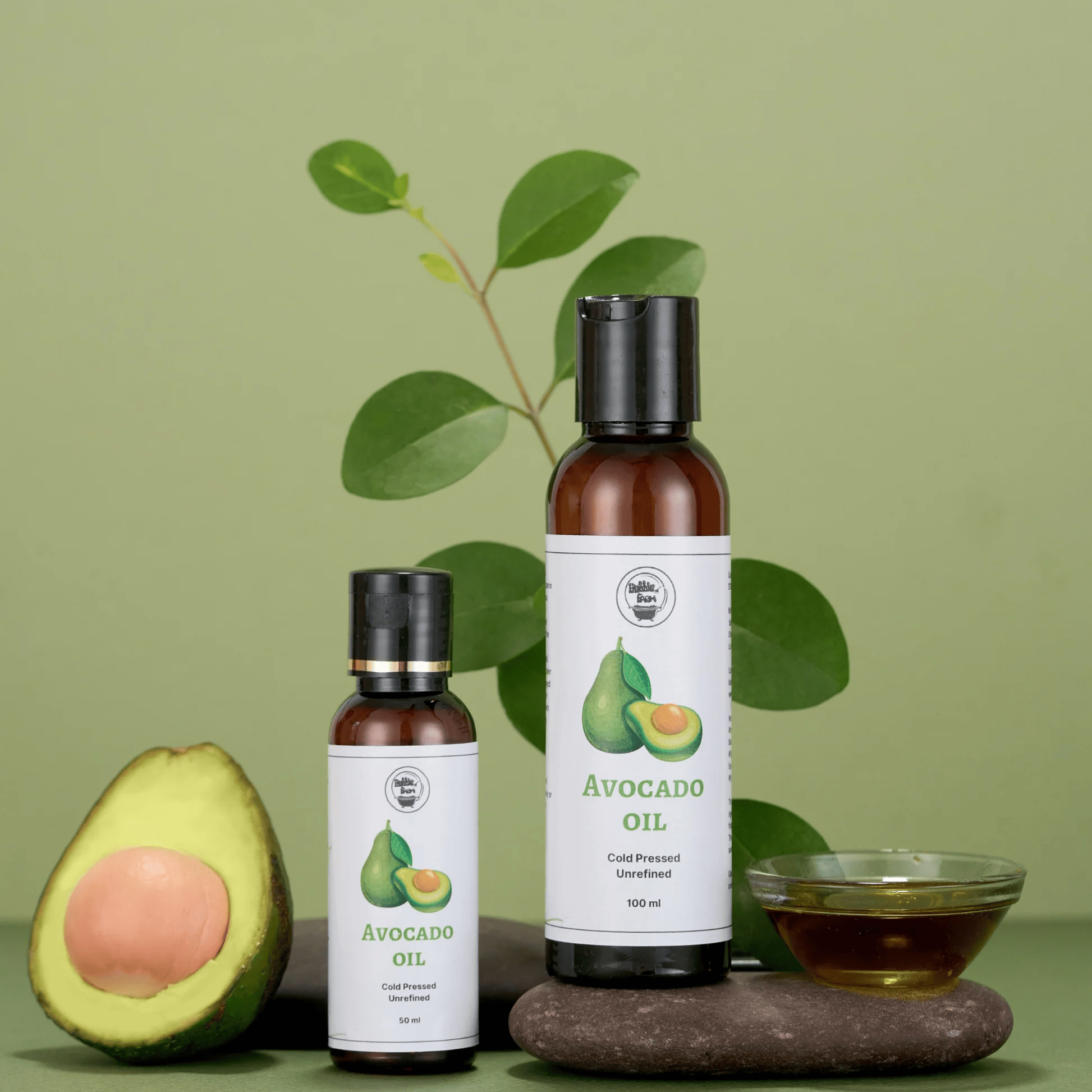

This trendy oil is packed with monounsaturated fats like oleic acid along with lutein and zeaxanthin powerful antioxidants that protect your eyes. Its high smoke point makes it ideal for high-heat cooking like stir-frying and grilling while its buttery flavor adds richness to salads and sauces.
3. Canola Oil:

Often dubbed the "all-purpose oil" canola oil is affordable neutral in flavor and boasts a high smoke point. It's rich in omega-3 fatty acids essential for brain and heart health and low in saturated fats. However some studies suggest potential downsides due to processing methods so look for organic cold-pressed options for optimal health benefits.
4. Coconut Oil:

This tropical oil has gained immense popularity for its unique fat profile. Composed mainly of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) coconut oil is readily absorbed by the body and used for energy rather than stored as fat. It also possesses antimicrobial properties and may boost metabolism. However its high saturated fat content should be considered when incorporating it into your diet.
5. Peanut Oil:

A favorite in Asian cuisine peanut oil has a high smoke point and nutty flavor making it ideal for stir-frying and deep-frying. It's rich in monounsaturated fats and contains resveratrol an antioxidant linked to numerous health benefits. However be mindful of peanut allergies if considering this oil.
6. Sesame Oil:

Toasted sesame seeds infuse this oil with a rich nutty aroma and taste perfect for Asian dishes marinades and dipping sauces. Sesame oil is a good source of vitamin E and lignans antioxidants with potential anti-inflammatory and cancer-fighting properties. Use it sparingly due to its strong flavor and lower smoke point.
Beyond the Big Six:
This is just a glimpse into the diverse world of cooking oils. Explore other options like grapeseed oil walnut oil and flaxseed oil for their unique flavor profiles and nutrient content. Remember moderation is key regardless of the oil you choose. Aim for a variety in your diet prioritizing healthy fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated and limiting saturated and trans fats.
Bonus Tip: When choosing an oil consider its smoke point the temperature at which it starts to burn and break down. Match the oil to your cooking method: low smoke point oils for salad dressings and dips medium for sautéing and high for deep-frying.
Oil Differentiation Based On Menu
1. Frying Chicken Thighs: Peanut Oil
- High Smoke Point: Peanut oil has a high smoke point making it perfect for frying chicken thighs to crispy perfection without burning.
- Neutral Flavor: Its subtle taste won’t overpower the flavor of your chicken ensuring that the seasoning remains the star of the dish.
2. Asian Dishes: Sesame Oil
- Rich Flavor: Sesame oil particularly toasted sesame oil adds a rich nutty flavor to Asian dishes enhancing the overall taste profile.
- Finishing Touch: Best used as a finishing oil in stir-fries or for dressing salads to retain its distinct flavor.
3. Deep Frying: Peanut Oil
- Stability at High Temperatures: Peanut oil can sustain high temperatures without breaking down making it ideal for deep frying.
- Reusable: It does not absorb the flavor of foods so you can reuse it multiple times for frying.
4. Stir Fry: Canola Oil
- Versatile Use: Canola oil's mild flavor and high heat tolerance make it a great all-purpose oil especially suitable for stir-frying.
- Health Benefits: Canola oil is low in saturated fats and contains beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
5. Air Frying: Oil Alternatives
- Minimal Oil Required: Air frying requires significantly less oil. Spraying a light coat of oil evenly over the food is often enough.
- Avocado Oil Spray: Use an avocado oil spray for its high smoke point and health benefits or opt for olive oil spray for a touch of flavor.
6. Baking: Coconut Oil
- Buttery Texture: Coconut oil can give baked goods a buttery texture without the use of dairy perfect for vegan recipes.
- Flavor Profile: Its slight coconut flavor works well in sweet baked goods like cakes and muffins.
7. Salad Dressings: Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Rich Flavor: Extra virgin olive oil adds a depth of flavor to salad dressings and is perfect for cold dishes.
- Health Properties: Rich in antioxidants and monounsaturated fats it's a healthy addition to any salad.
8. Sautéing Vegetables: Avocado Oil
- Nutrient Retention: Avocado oil's high smoke point ensures that vegetables can be sautéed at higher temperatures without losing nutrients.
- Subtle Flavor: Its mild taste won’t overpower the natural flavors of your vegetables.
Myths To Debunk On Choosing Right Cooking Oil!
When it comes to cooking oils there's a wealth of misinformation and myths that can lead to confusion. Understanding the truth behind these myths is crucial for making informed decisions about the oils you use in your kitchen. Let's debunk some common myths and shed light on the facts:
1. Myth: The Higher the Smoke Point the Healthier the Oil
- Reality: While a high smoke point is important for certain cooking methods like frying it doesn't necessarily mean the oil is healthier. Some oils with lower smoke points like extra virgin olive oil are packed with nutrients and beneficial compounds.
2. Myth: All Saturated Fats Are Bad for You
- Reality: Not all saturated fats are created equal. While it's true that excessive consumption of certain saturated fats can be unhealthy others like those found in coconut oil can be part of a healthy diet. Coconut oil contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) which are metabolized differently and can have health benefits.
3. Myth: “Light” Olive Oil is Lower in Calories
- Reality: The term “light” refers to the flavor and color of the oil not its calorie content. All oils have roughly the same amount of calories and fat per serving.
4. Myth: Vegetable Oils are Always a Healthy Choice
- Reality: While vegetable oils can be a good source of unsaturated fats not all are created equal. Some like canola oil are highly processed which can strip away nutrients and introduce harmful compounds. Opt for cold-pressed or minimally processed oils when possible.
5. Myth: Cooking with Olive Oil Releases Toxins
- Reality: This myth stems from the misunderstanding of the smoke point. While it's true that overheating olive oil (or any oil) can lead to the release of harmful compounds using olive oil for medium-heat cooking is perfectly safe and healthy.
6. Myth: You Can Reuse Frying Oil Many Times Without Any Consequences
- Reality: Repeatedly heating oil can increase the formation of harmful compounds. It's important to monitor the quality of oil if you're reusing it for frying. Look for signs of degradation like smoke off smells or a cloudy appearance.
7. Myth: Margarine is Always a Better Choice Than Butter
- Reality: Margarine became popular due to its lower saturated fat content compared to butter. However some margarines contain trans fats which are more harmful than the saturated fat in butter. It's important to read labels and choose margarine that's free of trans fats.
By debunking these myths you can make better choices about the cooking oils you use leading to healthier and more flavorful culinary experiences. Remember the key is moderation and variety – incorporating a range of healthy oils into your diet can provide diverse flavors and nutritional benefits.
Conclusion
Choosing the right oil for your dish is crucial in bringing out the best flavors and textures in your cooking. From the richness of sesame oil in Asian dishes to the versatility of canola oil in stir-fries each oil has its unique role. By understanding the smoke points and flavor profiles of different oils you can elevate your cooking to new heights. Remember debunking common myths about cooking oils will further refine your selection and enhance your culinary expertise. With this guide embark on a flavorful journey and make every dish a masterpiece.